
 |
Agricultural Profile of the Great Lakes |
| Stuart H. Gage |
Agriculture is a leading industry in the Great Lakes Basin. The Great Lakes Protection Fund recognized that to adequately understand the dynamics of agriculture in the Basin, it was important to develop a profile of the agricultural practices and trends in the Basin. A quatitative description of changes in agricultural practices and crop productivity trends are among the features that can characterize agriculture in the region. The agriculture profile project to develop characteristics and trends in production, land use and environmental impacts in the Great Lakes Basin was initiated in 1995. Gage, Co-PI at Kellogg LTER, played a role as advisor to the Agricultural Profile Team on trends in Greening using AVHRR and trends in Production of Corn in the Great Lakes Basin.
The objectives of the study were to build a digital database of information about argiculture in the Great Lakes and to provide a summary of trends in the Basin such that policy makers could develop better decisions based on sound information about the region.
The agricultural profile was organized into the following components: Resources in the Great Lakes Basin Ecosystem; Agriculture within the context of the Great Lakes Basin Ecosystem; The Nature of Agriculture in the Great Lakes Basin; and Trends and Their Impacts on the Great Lakes Basin Ecosyem. The focus of this document is to show telmpral changes within a season uning AVHRR imagery and the integration of Canadian and US agricultural crop statistics using corn production as an example. The AVHRR imagery was obtained through the LTER agreement with the EROS Data Center nad the crop production statistics was provided by the USDA and Agriculture Canada. The AVHRR imagery was processed using ESRI's Arc/Info and the county crop productivity statistics were mapped using Atlas*GIS, now an ESRI product.
The Agricultural profile document (cited below) provides an array of information about agriculture in the Greal Lakes. In general terms, four general land use classes exist in the Basin. Forests occupy 42%.(318,000 sq km); agriculture ,24% (172,000 sq km); water, 33% and urban lands occupy 1% of the area. Corn is the dominant crop occupying 35% of the cropland. Changing population abundance amd land use demands are placing pressures on land use.
The following sequence is developed from AVHRR imagery from April-August, 1993. Data were extracted from CD-Rom composite images provided to LTER sites via the LTER Network Office.
Great Lakes Vegetation change based on AVHRR composite imagery
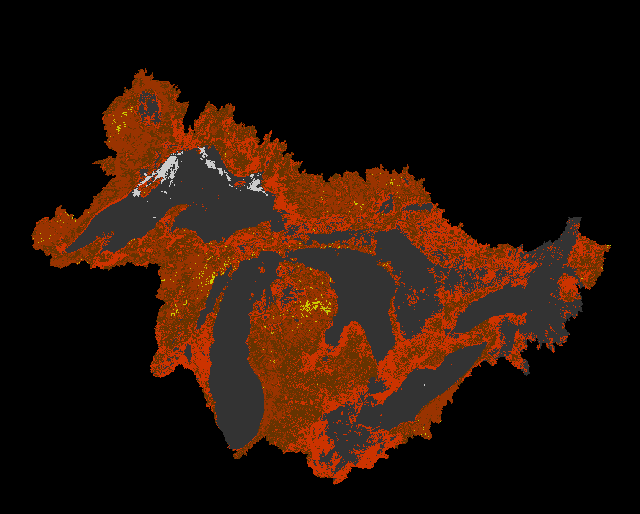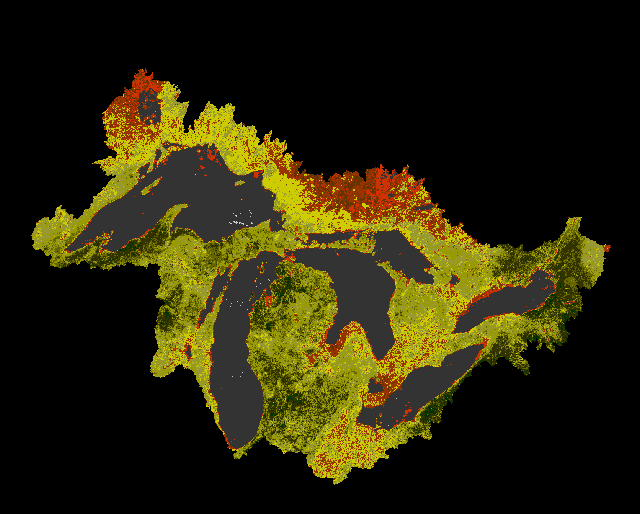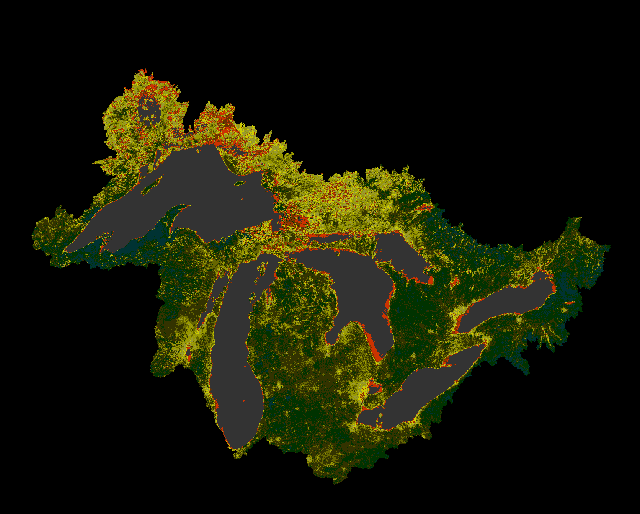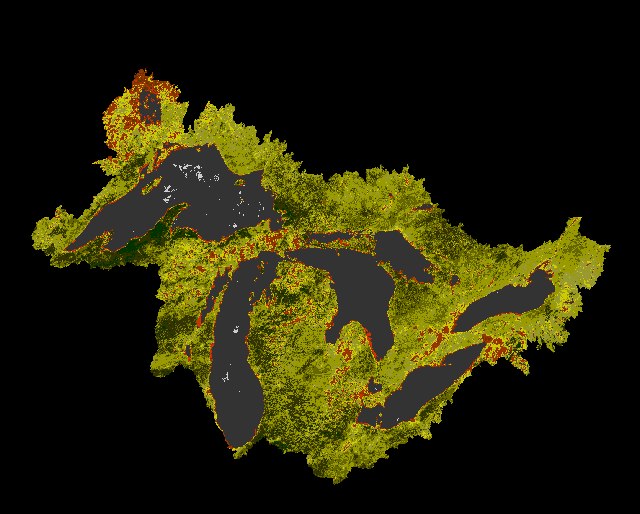 |
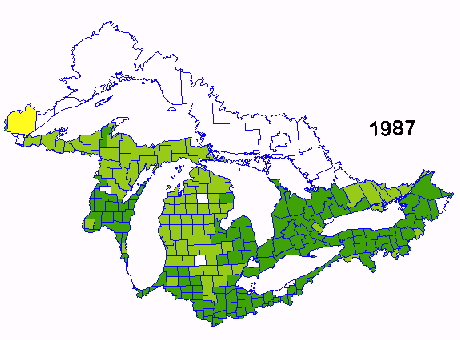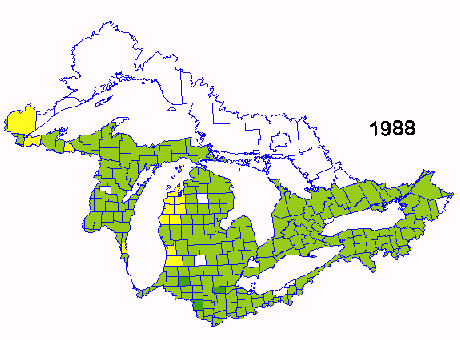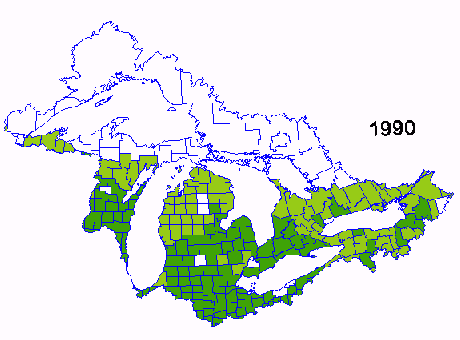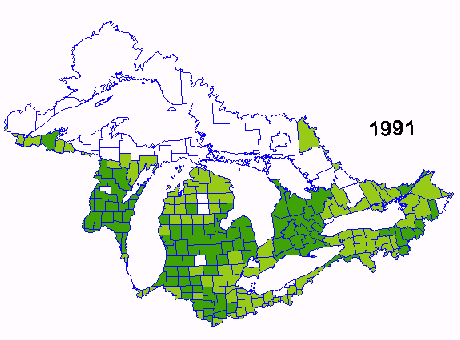
Corn Yield per acre from 1987-1991
Corn is one of the major crops grown in the Great Lakes Basin. Data for this sequence of images of corn yield was obtained from the USDA and Agriculture Canada. The sequence spans 1987-1991 and shows the variability in yield due the weather and other management factors. The yield in 1987 was one of the best in 20 years and yields in 1988 were the poorest during the same period due to reduced precipitation during may and June.
 |
Michigan State University, Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada, World Wildlife Fund, University of Guelph, Radian Corporation, Great Lakes Commission, Advisory Committee, Natural Resources Conservation Service.
Agricultural Profile Project Team. 1995. An agriculture profile of the Great Lakes Basin: characteristics and trends in production, land use and environmental impacts Compiled by the Great Lakes Commission. Ann Arbor, MI. 330 pp.
Great Lakes Information System
Top | KBS Regionalzation | KBS LTER home page | The LTER network
For information contact: gages@pilot.msu.edu
Document author(s): Stuart Gage
E-Mail: gages@pilot.msu.edu
Revised: December 09, 1996
URL: http://www.ent.msu.edu/esal/lter_region